Learning objectives
- identify organisms using diagnostic features of the five Kingdoms
- use diagnostic features to divide kingdoms into phyla
- state the taxonomic hierarchy.
- observe the rules of binomial nomenclature
Introduction #
- Diversity is the variety of living organisms
- Organisms have been grouped together for studies of their characteristics
- The grouping of organisms is called classification
- classification is based on agreed name of each organism
Hierarchy of classification #
- Systems of classification are hierarchical i.e each successive group contains more and more different kinds of organisms.
- Taxon is the general name given to each classification grouping.
- Taxonomy is the science of classification of organisms into groups called taxons
- The longest taxon is the species and the most increasing or highest taxon is the kingdom.
- Phylogeny is the study of evolutionary traits.
- Natural classification of organisms is based on evolutionary relationships.
Terminology #
- Kingdom is the largest grouping of organisms e.g animalia
- Phylum consists of organisms with many similarities e.g bryophyte, cnidarians etc.
- Class consists of organisms which are grouped into several orders with few similarities
- Order is a group of apparently related families
- Family is a group of apparently related genera
- Genus is a group of similar and closely related species
- Species is a group of organisms capable of interbreeding to produce fertile off springs
Binomial nomenclature #
- in this system each organism has two latin names, a generic name first capitalised and the specific name with a lowercased later
- the latin name is internationally agreed and avoid the confusion of local variation in local names
- eg humans are named Homo sapiens
genus-homo
species-sapiens - The generic name is shared with other related species considered to be sufficiently similar to be grouped in the same genus e.g Homo erectus, Homo habilis
The taxonomic hierarchy #
- Linnaeus extended binomial system of classifying organisms to introduce more groups than just the genus and species
- there are arranged in a hierarchy with the largest group the kingdom at the top to the species.
- kingdom → phylum → class → order → family → Genius → species
Specimen identification and keys #
- A key is a method for identifying an organism by listing observable characteristics and matching them to diagnostic features of a group.
- Keys rely on easily observable features like shape, color, number of appendages, etc. So identification is artificial and phenetic, based purely on appearance (phenotype).
- Despite this, keys enable organisms to be identified into groups that are part of a natural phylogenetic classification system.
- A dichotomous key consists of paired contrasting and mutually exclusive statements (leads) about characteristics, which break down organisms into smaller groups.
- Characteristics used should be observable morphological features, qualitative (e.g. shape) or quantitative (e.g. number of hairs).
- Chosen characteristics should exist in two or more states (e.g. stem shape: round or square).
- Each statement is followed by a number referring to the next lead to consider if the statement matches the specimen.
- This stepwise process continues until the unknown organism is identified.
The Five kingdoms #
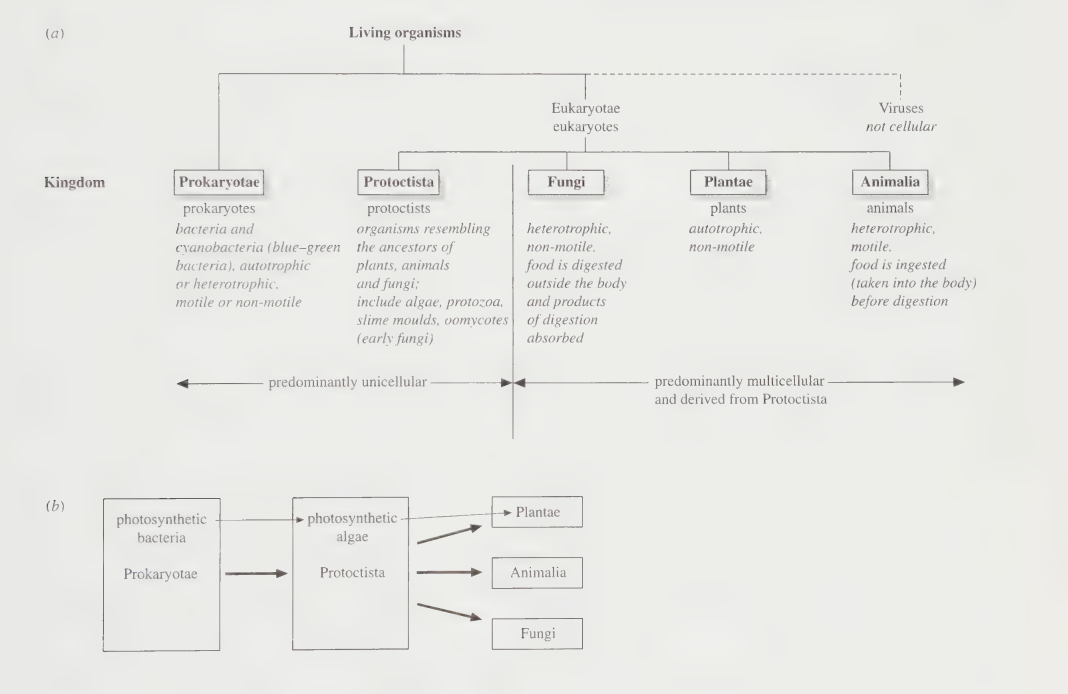
Advantages of Five Kingdom Classification #
- We can study the characteristics of organisms by only looking at a few members of a particular kingdom.
- Classifying organisms makes it simpler and easier to understand their traits.
- It helps trace origin and study growth patterns, reproduction, structure, and survival needs.
- The Five Kingdom System also divides unicellular and multicellular organisms into different groups.

